EYE: “A clue to diagnosis”
K V K S N Murthy, Madhura Prasad, Mithra Prasad and V G Mohan Prasad
Cite this article as: BJMP 2015;8(2):a817
|
A 38 year male presented to our centre with a two-month history of jaundice. Past medical & family history was insignificant. Clinical examination revealed a icterus and greenish brown ring in both eyes (Figure 1). Laboratory investigations revealed a mild thrombocytopenia (platelet count-1.2 lakh/mm3) and a prolonged prothrombin time. Liver function tests showed elevated serum levels of alanine aminotransferase & aspartate aminotransferase. Serology for hepatotropic viruses was negative. Serum ceruloplasmin was 9.8 mg/dl (reference range 20-60mg/dl) and 24 hour urinary copper was elevated.
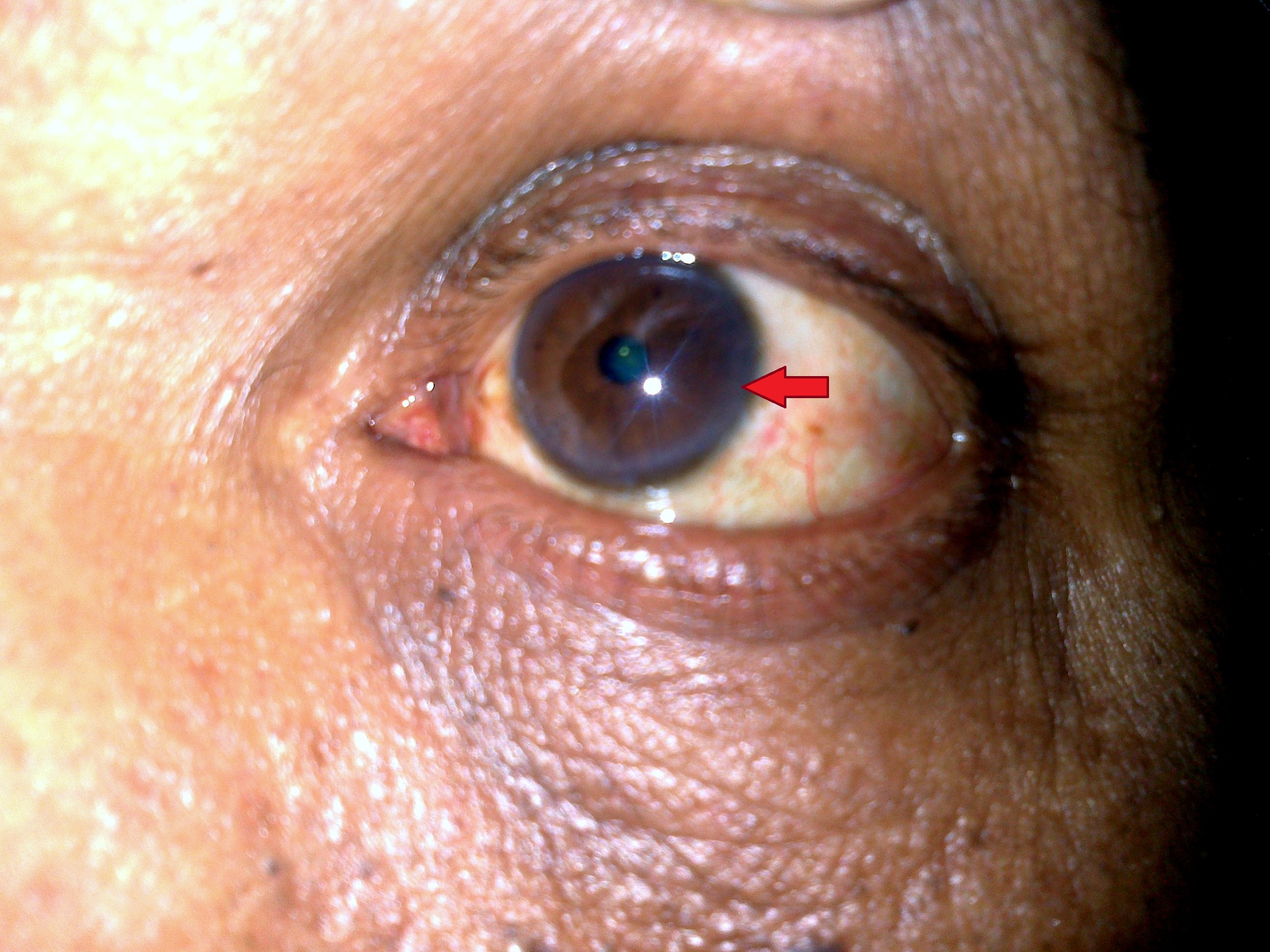
Figure 1
What is the eye finding?
- Arcus Senilis
- Pterygium
- Kayser Fleischer ring
- Phlycten
Correct Answer:
3. Kayser Fleischer ring
Discussion:
Wilson’s disease is a consequence of defective biliary excretion of copper. This leads to its accumulation in the liver and brain 1. It is due to mutations of the ATP7B gene on chromosome 13, which codes for a membrane-bound copper transporting ATPase 2.
Kayser-Fleischer ring is an outcome of abnormal copper deposition in the membrane in the limbus of cornea. Slit-lamp examination by an experienced observer is required to identify a K-F ring. The colour may range from greenish gold to brown. When well developed, a K-F ring may be readily visible to the naked eye. K-F ring is observed in most individuals with symptomatic Wilson disease and are almost invariably present in those with neurologic manifestations. They are not entirely specific for Wilson’s disease, since they may also be found in patients with chronic cholestatic diseases.
Clinical presentation is variable and patients presenting with chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis & at times acute liver cell failure. The most common presenting neurologic feature is asymmetric tremor. The characteristic tremor is coarse, irregular proximal tremulousness with a “wing beating” appearance.
Typically, the combination of K-F rings and a low serum ceruloplasmin (<0.1 g/L) level is sufficient to establish a diagnosis of Wilson’s disease 3. However delayed diagnosis in patients with neuropsychiatric presentations is frequent and was in one case as long as 12 years 4.Our patient was treated with a none copper diet, oral zinc and d pencillamine. His liver functions became normal over 6 months of treatment and without progression of liver disease.
Arcus Senilis is a grey band of apacity near the sclero-corneal margin, commonly found in the elderly and associated with hypercholesterolemia. Pterygium is a benign wedge shaped fibrovascular growth of conjunctiva that extends onto the cornea. Phylecten is consequence of allergic response of the conjunctive & corneal epithelium usually associated with tuberculosis, staphylococcus protein and moraxella.
|
Competing Interests None declared Author Details K V K S N MURTHY, MBBS, MD, (DM Gastroenterology), Registrar, Department of Gastroenterology, VGM Hospital & Institute of Gastroenterology, Coimbatore , India. MADHURA PRASAD, MBBS, MD Internal Medicine, DNB Gastroenterology, VGM Hospital & Institute of Gastroenterology, Coimbatore , India. MITHRA PRASAD, MBBS, MD Internal Medicine, VGM Hospital & Institute of Gastroenterology, Coimbatore , India. V G MOHAN PRASAD, MBBS, MD, DM Gastroenterology, MIASL, FCCP, FAGE, Chairman, VGM Hospital & Institute of Gastroenterology, Coimbatore , India. CORRESPONDENCE: Dr. K V K S N Murthy, MBBS, MD, (DM Gastroenterology), Registrar, Department of Gastroenterology, VGM Hospital & Institute of Gastroenterology, Coimbatore , India. Email: vamsikiran9@gmail.com |
References
- Gitlin JD. Wilson disease. Gastroenterology 2003;125:1868–1877.
- Tao TY, Gitlin JD. Hepatic copper metabolism: insights from genetic disease. Hepatology 2003;37:1241–1247.
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson’s disease. Journal of Hepatology 2012 vol. 56; pg 671–685.
- Merle U, Schaefer M, Ferenci P, Stremmel W. Clinical Presentation, diagnosis and long-term outcome of Wilson disease – a cohort study. Gut 2007;56:115–120.

The above article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.




